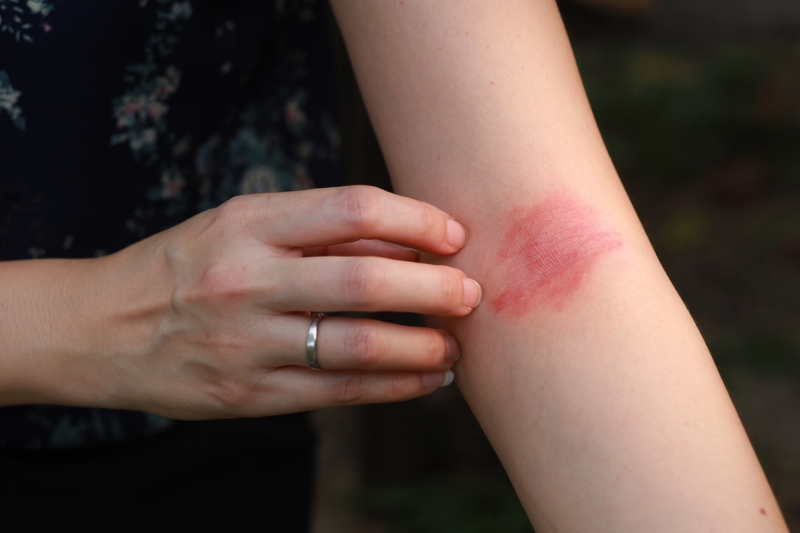
Eczema, a persistent skin condition, can present an enduring source of discomfort and emotional distress for individuals with symptoms. The daily battle against itching and irritation can disrupt lives both physically and emotionally.
Despite the countless treatments, there’s a natural remedy that’s been gaining recognition for its undermined healing abilities: mānuka oil.
What Is Mānuka Oil?
Mānuka oil, derived from the leaves and branches of the Mānuka tree (Leptospermum scoparium), is celebrated for its exceptional therapeutic properties. This essential oil is known for its potent antimicrobial properties, making it highly effective in addressing various skin concerns.
Often referred to as the ‘Tea Tree’ of New Zealand, manuka oil is also useful for its analgesic, antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, deodorant, expectorant, immune tonic, insecticidal and sedative properties.
The Origin of Mānuka Oil

Mānuka oil hails from New Zealand where the mānuka tree thrives in the pristine environment. The Māori people, the indigenous inhabitants of New Zealand, have utilized mānuka oil for generations due to its remarkable healing properties.
Is Mānuka Oil Good for Eczema?
Mānuka oil has received considerable recognition for its effectiveness in managing eczema.
Mānuka oil possesses a unique combination of anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties that make it particularly well-suited for alleviating the discomfort associated with eczema. Its anti-inflammatory capabilities help reduce redness and swelling, while its antibacterial nature can prevent infections, especially in cases where the skin is compromised. Furthermore, mānuka oil’s moisturizing qualities contribute to soothing dry, flaky skin.
Understanding Eczema: Signs, Symptoms, and Types
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation, itching, and irritation of the skin. While the exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, it is widely acknowledged and substantiated by the National Eczema Association that a combination of genetic and environmental factors influences the condition.
Signs and Symptoms of Eczema
The signs and symptoms of eczema can vary from person to person but often include:
- Itchy Skin: Pruritus, or intense itching, is the hallmark symptom of eczema. It can be severe, leading to scratching, which can further worsen the condition.
- Redness: Affected skin areas typically appear red or inflamed.
- Dryness: Eczema-prone skin is often dry, scaly, and may feel rough to the touch.
- Rash: Eczema can cause the development of a rash with small, raised bumps that may ooze fluid and become crusty when scratched.
- Swelling: In some cases, the skin can become swollen and puffy.
- Thickened Skin: Prolonged inflammation can lead to thickened and leathery skin in the affected areas, especially if the condition is chronic.
Types of Eczema
There are several types of eczema, each with distinct characteristics and triggers. Here are some common types of eczema:
- Atopic Dermatitis: Atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema and is often associated with allergies and a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever. It typically presents with red, itchy skin and is common in children but can persist into adulthood.
- Contact Dermatitis: Contact dermatitis is caused by exposure to irritants or allergens, such as certain soaps, detergents, fragrances, plants like poison ivy, or metals like nickel. It is characterized by redness, itching, and a rash at the site of contact.
- Nummular Eczema: Nummular eczema appears as coin-shaped, raised patches of irritated skin. It can be triggered by dry skin, environmental factors, or allergens.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Seborrheic dermatitis typically affects areas with more oil-producing glands, such as the scalp and face. It can lead to redness, itching, and flaking of the skin.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Dyshidrotic eczema mainly affects the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. It is characterized by the development of small, itchy blisters that can be triggered by factors like stress, allergies, or exposure to irritants.
- Stasis Dermatitis: Stasis dermatitis occurs in areas with poor blood circulation, often in the lower legs. It can result from conditions such as varicose veins and is characterized by redness, swelling, and skin changes.
- Neurodermatitis: Neurodermatitis is a type of eczema characterized by thickened, leathery patches of skin that result from repeated scratching and rubbing.
Mānuka Oil for Eczema: Benefits and Uses
Some of the benefits of mānuka oil for eczema that have been explored in scientific studies include:
- Antimicrobial Properties: Mānuka oil contains compounds like β-triketones that exhibit antimicrobial properties, helping to prevent bacterial and fungal infections in eczema-prone skin, which is vulnerable to secondary infections due to scratching and broken skin.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Mānuka oil’s anti-inflammatory properties can alleviate redness and swelling associated with eczema, providing relief from discomfort.
- Soothing and Moisturizing: Mānuka oil helps soothe irritated skin and provides much-needed moisture to dry, eczema-prone areas, contributing to skin comfort.
When using mānuka oil for eczema, it’s crucial to dilute it properly with a carrier oil and perform a patch test to check for skin sensitivity. Consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist for personalized advice tailored to your specific eczema condition.
Other Mānuka Oil Benefits for Skin
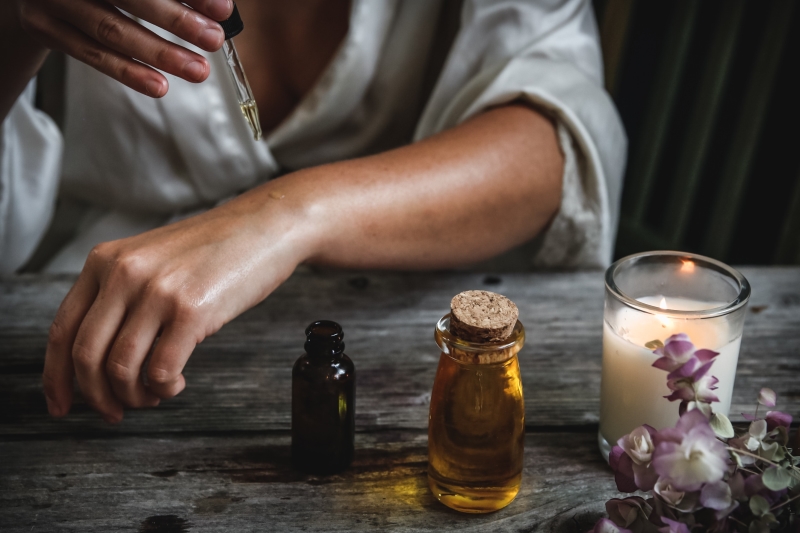

A natural ally in the pursuit of healthier skin, mānuka oil offers a range of potential benefits for skin health beyond its use for eczema management. Here are some of the manuka oil skin benefits:
- Acne Treatment: Mānuka oil’s antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties make it effective for treating acne by reducing the growth of acne-causing bacteria and calming inflammation.
- Wound Healing: Mānuka oil aids in wound healing by preventing infections in minor cuts, burns, and abrasions, while reducing redness and swelling.
- Skin Infections: The antimicrobial properties of mānuka oil make it useful for treating various skin infections, including fungal conditions like athlete’s foot and ringworm. It can be applied topically to affected areas.
- Skin Rejuvenation: Adding mānuka oil to skincare products promotes skin rejuvenation by stimulating collagen production and supporting skin regeneration, potentially improving the appearance of scars, fine lines, and wrinkles.
- Dandruff and Scalp Health: Mānuka oil can be incorporated into shampoos or scalp treatments to address issues including dandruff, dryness, flakiness, and itching.
- Aromatherapy: In addition to topical use, mānuka oil can be used in aromatherapy to reduce stress and promote relaxation. Diffusing mānuka oil creates a calming atmosphere that benefits overall skin health.